
Noise-induced hearing loss is the most common permanent but preventable occupational injury. Unlike other injuries, there is no visible evidence.
Since it's not traumatic, if often goes unnoticed until it's too late. Prevent on the job hearing loss by wearing proper ear protection!
Shop All Hearing Protection Here and if you can’t find what you’re looking for, give us a call at 800-525-3313.
Style Options

Foam
they are compressed into the ear canal where
they expand until a seal is formed. Disposable
or used for a limited amount of time.

Push In/Pod
Features a built-in central stem to push
the plugs into the ear canal. These earplugs
achieve a seal due to their tapered shape
rather than their expansion after being rolled. Disposable or used for a limited amount of time.

Flanged
Also called reusable earplugs because they can
be cleaned and reused. They come with a firm
stem and tapered shape for easy insertion. The
soft flanges provide an excellent barrier protecting workers from loud levels of noise.
Banded
hazards. A cooler and lighter alternative to
earmuffs. Features soft foam pod tips.
.jpg)
Earmuffs
Noise blocking earmuffs are designed to offer consistent attenuation, rugged construction and worker comfort. They come in cap-mounted, folding, over-the-head, behind-the-head, below-the-chin and conventional styles.
Proper Foam Earplug Insertion
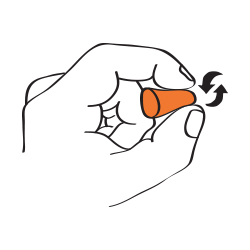
Step One
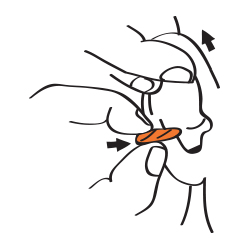
Step Two
Reach over your head with your free hand, pull
your ear up and back, and push the earplug well
inside your ear canal. Stop pushing when your
finger touches your ear.
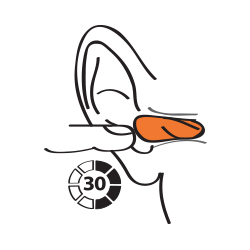
Step Three
Hold for 30 – 40 seconds, until the earplug fully expands in your ear canal. If properly fitted, the
end of the earplugs should not be visible to
someone looking at you from the front.
Acoustical Check
Noise Reduction Rating
Noise reduction rating is the most standardized method currently in use for describing a hearing protector’s attenuation in a single number. The current range of NRRs
available range from 0 to 33 decibels. The NRR estimates the amount of protection achievable by 98% of users in a laboratory setting when hearing protectors are properly fitted.
OSHA CFR 1910.95 Standard
OSHA CFR 1910.95 requires employers first to utilize “engineering controls” to reduce noise levels in their work environments. If these controls fail to
reduce noise levels to acceptable limits, the regulations state that “personal protective equipment shall be provided and used to reduce sound levels”.

